Science Report – August 4th
HAUGHTON IMPACT STRUCTURE AND EVIDENCE OF PRIMITIVE LIFE
By Anushree Srivastava – Crew Biologist
Investigating the impact-induced hydrothermal gypsum deposits in Haughton Impact crater is one of my principal objectives as Mars-based scientist. With our Crew Geologist Dr Jon Clarke and our Earth-based scientist Dr Alfonso Davila of NASA Ames Research Centre and SETI Institute, I am conducting this study to understand the possibility of any preserved biosignatures in those hydrothermal sulfates. Haughton Impact structure was carved when a large rock collided with the earth about 39 million years ago near what we call now the Canadian High Arctic (75°22’N, 89°41’W). The 24 km diameter crater lies in Devon Island that is described as the largest uninhabited island in the world.
Impact craters have always been the hot spots for astrobiologists to look for the preservation of life via volcanic or hydrothermal processes and to establish an analogy for extraterrestrial sites where primitive life could evolve and preserved. The Miocene Haughton structure hosts the well-preserved history of impact-generated hydrothermal activity and sulfate crystallization. Gordon Osinski, Pascal Lee and Charles Cockell have extensively studied and documented the sulfate deposits of Haughton crater. Interestingly, they demonstrated the microbial colonization in sulfate crystals and those microbes further modify the structure of the crystal to find a favourable niche to survive. Those microbial communities were found to be grown in situ and identified primarily as cyanobacteria.

Figure 1: Cell structure of cyanobacteria growing in situ in gypsum crystals. (Parnell et al., 2005)
So, Dr Jon Clarke and I planned an extra-vehicular activity (EVA) to the site which is described as “impact supersite” by Gordon Osinski. The supersite is located near the middle of the Haughton crater and is about 10 km drive from FMARS. I intended to sample the sulfate deposits from the supersite to investigate any viable or fossilized signatures of life originated and thrived during impact-induced hydrothermal event in the past. We sampled gypsum-bearing evaporites from outcrops belong to the mid-Ordovician Bay Fiord Formation (39 mya). According to Thorsteinsson et al (1987) Bay Fiord Formation is mainly composed of limestone/dolomite and of argillaceous/silty and evaporitic nature. The Formation is divisible in four members and have been categorised as A to D. Only the member A consists of gypsum/anhydrite deposition.
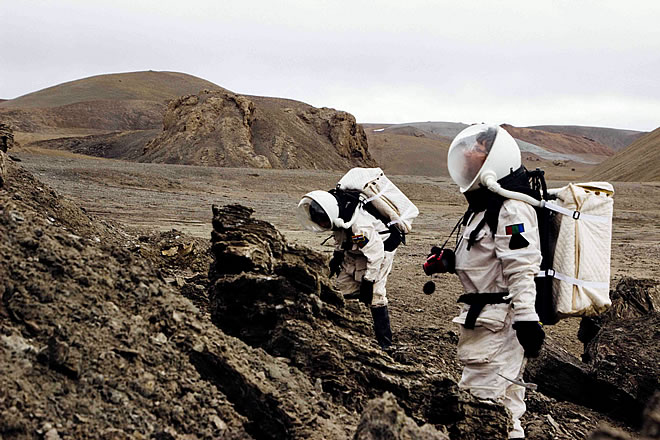

Figure 2: Anushree and Jon on EVA investigating gypsum beds. (Image Credit: Paul Knightly)
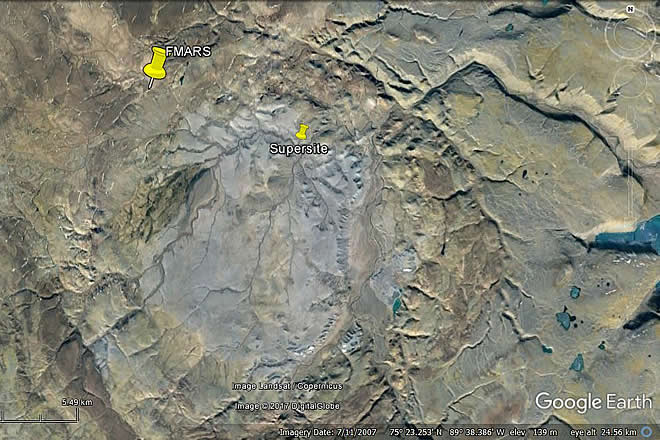
Figure 3: Haughton Impact crater. Indicating FMARS and Hydrothermal Supersite. Sulfates are one of the prominent salt species that have been detected on Mars.
In the Bay Fiord Formation the gypsum was deposited through evaporation of seawater. Elsewhere in the crater gypsum is known to have formed as a result of the impact driven hydrothermal activity. Both the processes are considered to be analogous to the sulfate precipitation from the low-temperature aqueous fluid on Mars. So, any microbial life that was present in the brine could have found refuge in tiny fluid-inclusions of the gypsum crystals in the past or potentially left their marks in the depository layers while degradation. Hence, it is fascinating to explore the idea
of preservation of biomarkers in evaporite rocks.
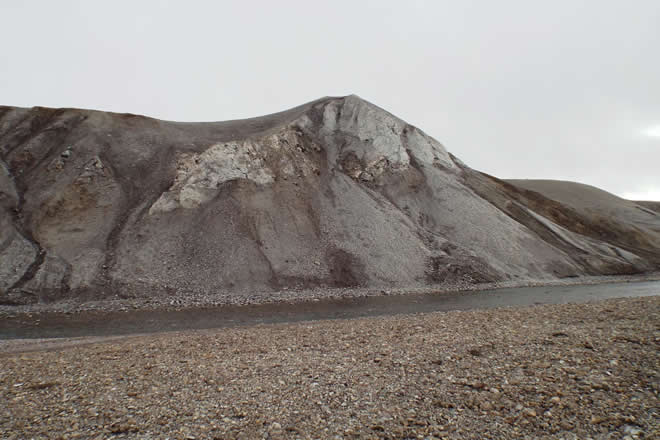

Figure 4: Impact Supersite. (Image Credit: Dr Jon Clarke)
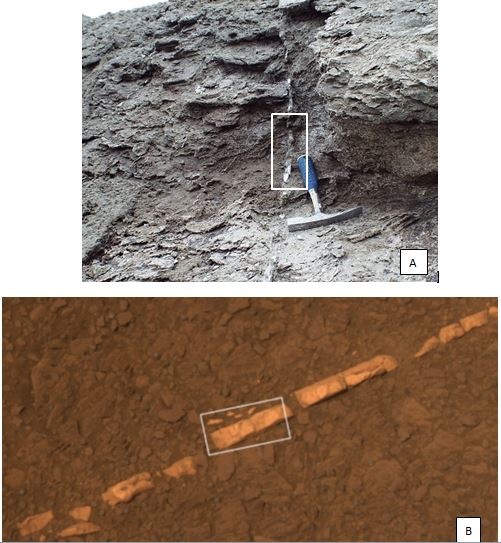

Figure 5: A. Gypsum veins at Hydrothermal Supersite in Devon Island (Image Credit: Dr Jon Clarke). B. Gypsum veins at the Endeavour Crater on Mars (Image Credit: NASA JPL/Caltech).
Further Readings:
Cockell, C. S., Osinski,G. R., Banerjee, N. R., Howard, K. T., Gilmour, I., and Watson, J.S. 2010. The microbe–mineral environment and gypsum neogenesis in a weathered polar evaporite. Geobiology 8, 293–308.
Mayr, U., de Freitas, T., Beauchamp, B., and Eisbacher,G. 1998. The Geology of Devon Island North Of 76°, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin 526, 500p.
Morrow D. W. and Kerr, J. W. 1977. Stratigraphy and sedimentology of Lower Paleozoic Formations near Prince Alfred Bay, Devon Island. Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin 254, 122p.
Parnell et al 2005. Microbial Preservation in Sulfates in the Haughton Impact Structure suggest target in search for microbial life on Mars. Lunar and Planetary Science XXXVI
Squyres et al 2012. Ancient Impact and Aqueous Processes at Endeavour Crater, Mars. Science 336, 570-575p.
Thorsteinsson, R. and Mayr, U. 1987. The sedimentary rocks of Devon Island, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin 411, 182p.